Get ready to dive into the world of compounding interest where your money can grow exponentially over time. Imagine a scenario where your initial investment keeps multiplying like a high school rumor, gaining momentum and creating wealth beyond your expectations. Let’s explore this financial phenomenon and how it can work wonders for your long-term financial goals.
Now, let’s break down the concept of compounding interest and see how it can supercharge your finances.
Definition of Compounding Interest
Compounding interest is the process where the interest on a loan or investment is calculated based on the initial principal as well as the accumulated interest from previous periods. This is in contrast to simple interest, where interest is only calculated based on the principal amount.
How Compounding Interest Works
When you invest money in an account that earns compound interest, your earnings begin to grow exponentially over time. This is because the interest you earn is added to your principal, and future interest calculations are based on the larger amount.
- For example, if you invest $1,000 in an account with an annual compounding interest rate of 5%, at the end of the first year you will have $1,050. In the second year, you will earn 5% interest not just on your initial $1,000 but also on the $50 interest you earned in the first year.
- Over time, this compounding effect can significantly increase the value of your investment, allowing your money to grow faster than it would with simple interest.
Importance of Compounding Interest in Financial Planning
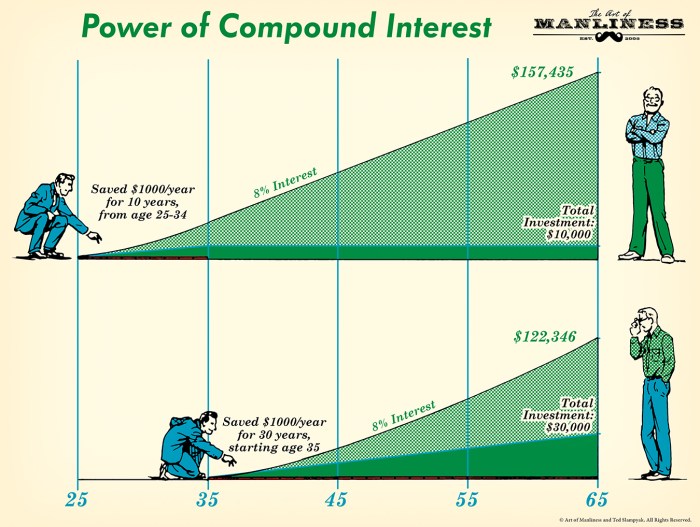
Understanding the power of compounding interest is crucial for long-term financial planning. By starting to invest early and allowing your money to compound over time, you can build substantial wealth for the future.
“Compound interest is the eighth wonder of the world. He who understands it, earns it. He who doesn’t, pays it.” – Albert Einstein
Formula for Calculating Compounding Interest
When it comes to calculating compounding interest, there is a specific formula that is commonly used. This formula takes into account the initial principal amount, the interest rate, the number of compounding periods per year, and the time the money is invested for.
Understanding the Formula
The formula for calculating compound interest is as follows:
Compound Interest = P(1 + r/n)^(nt) – P
Where:
– P is the principal amount (initial investment)
– r is the annual interest rate (in decimal form)
– n is the number of times that interest is compounded per year
– t is the time the money is invested for, in years
Step-by-Step Example
Let’s say you invest $1,000 at an annual interest rate of 5%, compounded quarterly for 3 years. Using the formula, we can calculate the compound interest earned on this investment.
- Identify the values:
– P = $1,000
– r = 0.05
– n = 4 (quarterly compounding)
– t = 3 years - Plug the values into the formula:
Compound Interest = $1,000(1 + 0.05/4)^(4*3) – $1,000 - Calculate inside the parentheses first:
1 + 0.05/4 = 1.0125 - Raise the result to the power of (4*3 = 12):
(1.0125)^12 = 1.191017 - Calculate the compound interest:
$1,000 * 1.191017 – $1,000 = $191.02
Therefore, the compound interest earned on a $1,000 investment at 5% interest rate compounded quarterly for 3 years would be $191.02.
Types of Compounding Frequencies
When it comes to compounding interest, the frequency at which interest is calculated and added to the principal can have a significant impact on the final amount earned. Different compounding frequencies, such as annually, semi-annually, quarterly, monthly, and daily, can affect the overall growth of an investment.
Annually
- Interest is calculated and added to the principal once a year.
- Less frequent compounding can result in lower overall returns compared to more frequent compounding.
- Investors who prefer simplicity and don’t need immediate access to their funds may opt for annual compounding.
Semi-Annually
- Interest is calculated and added to the principal twice a year.
- More frequent compounding than annual compounding, leading to slightly higher returns.
- Can be a good middle ground for investors looking for a balance between growth and accessibility.
Quarterly
- Interest is calculated and added to the principal four times a year.
- Even more frequent compounding than semi-annual, resulting in higher returns.
- Suitable for investors seeking accelerated growth and willing to lock in their funds for a period.
Monthly
- Interest is calculated and added to the principal twelve times a year.
- Highly frequent compounding leading to significant growth over time.
- Preferred by investors aiming for maximum returns and willing to commit to a long-term investment strategy.
Daily
- Interest is calculated and added to the principal every day.
- The most frequent compounding frequency, offering the highest potential for growth.
- Suitable for investors with a high-risk tolerance and a long-term investment horizon.
Benefits of Compounding Interest
When it comes to building wealth, compounding interest is the key player in the game. This powerful concept allows your money to grow exponentially over time, turning small investments into substantial sums through the magic of reinvesting your earnings.
Compounding interest accelerates wealth accumulation by not only earning interest on your initial investment but also on the interest you’ve already earned. This snowball effect can lead to significant growth in your investment portfolio over the long run, without you having to lift a finger.
Accelerated Growth
- Imagine you invest $1,000 in an account that offers a 5% annual interest rate compounded annually. After the first year, you would earn $50 in interest, bringing your total to $1,050. In the second year, you earn 5% interest not just on your initial $1,000 but on the $50 interest from the previous year, resulting in $52.50 in interest. This cycle continues, and you start to see your money grow faster and faster each year.
- Over time, the compounding effect can lead to substantial wealth accumulation. For instance, if you were to invest $100 per month in an account with an 8% annual interest rate compounded monthly for 30 years, you could potentially amass over $100,000 in savings, with the majority of it coming from the compounding interest.
Strategies for Maximizing Compounding Interest
When it comes to maximizing compounding interest returns, there are several key strategies that can help you make the most out of your investments.
Start Early and Stay Consistent
One of the most important strategies for maximizing compounding interest is to start investing early and stay consistent with your contributions. The earlier you start investing, the more time your money has to grow through compounding. Consistency in making regular contributions can also significantly boost your returns over time.
Diversify Your Investments
Diversifying your investments across different asset classes can help you maximize compounding interest returns while reducing risks. By spreading your investments across various sectors, you can benefit from growth in different areas of the market and protect your portfolio from potential downturns.
Reinvest Your Earnings
Another effective strategy for maximizing compounding interest is to reinvest your earnings back into your investments. By reinvesting the interest or dividends you earn, you can accelerate the growth of your portfolio and take advantage of the power of compounding to generate even higher returns over time.
Take Advantage of High-Compounding Investments
Exploring investment options that offer high compounding returns, such as dividend-paying stocks, growth-oriented mutual funds, or tax-advantaged retirement accounts, can help you maximize the power of compounding interest. These investments have the potential to generate significant returns over the long term, allowing you to benefit from compounding to its fullest extent.
