With financial asset classes at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights.
When it comes to building wealth and securing your financial future, understanding different asset classes plays a crucial role. From stocks to real estate, each class offers unique opportunities and risks that can impact your investment decisions. Let’s dive into the world of financial asset classes and explore the key aspects that every investor should know.
Overview of Financial Asset Classes
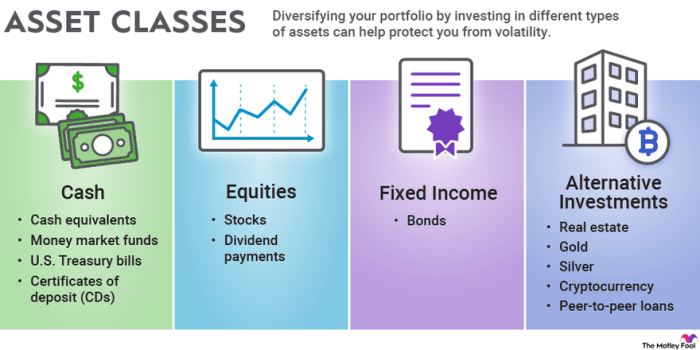
Financial asset classes refer to different categories of assets that investors can invest in, each with unique characteristics and risk-return profiles. It is essential for investors to understand these asset classes to diversify their portfolios effectively and achieve their financial goals.
Equities
Equities represent ownership shares in a company, also known as stocks. Investing in equities can provide investors with potential capital appreciation and dividends. Examples include shares of companies like Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon.
Bonds
Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations to raise capital. Investors who purchase bonds are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of the principal amount at maturity. Examples include U.S. Treasury bonds, corporate bonds, and municipal bonds.
Real Estate
Real estate investments involve purchasing properties such as residential homes, commercial buildings, or land. Investors can generate income through rental payments or capital appreciation. Examples include rental properties, real estate investment trusts (REITs), and vacant land for development.
Commodities
Commodities are physical goods that can be bought and sold, such as gold, silver, oil, and agricultural products. Investing in commodities can provide diversification benefits and a hedge against inflation. Examples include gold bullion, crude oil futures, and agricultural ETFs.
Alternative Investments
Alternative investments encompass a wide range of assets beyond traditional stocks and bonds, including hedge funds, private equity, venture capital, and cryptocurrencies. These investments often have unique risk-return profiles and can offer opportunities for higher returns but come with higher risk levels.
Types of Financial Asset Classes
Investing in financial asset classes is a key strategy for building wealth and achieving financial goals. There are several main categories of financial asset classes, each with its own unique characteristics and features. Let’s explore the main types of asset classes and compare their risk-return profiles.
Stocks
Stocks represent ownership in a company and are also known as equities. Investors buy shares of stock in the hope that the company will grow and increase in value over time. Stocks have the potential for high returns but also come with higher risk due to market volatility.
Bonds
Bonds are debt securities issued by governments, municipalities, or corporations to raise capital. When you invest in bonds, you are essentially lending money to the issuer in exchange for periodic interest payments and the return of the principal at maturity. Bonds are generally considered less risky than stocks but offer lower returns.
Real Estate
Real estate investments involve purchasing physical properties such as residential homes, commercial buildings, or land. Real estate can provide a steady income stream through rental payments and potential capital appreciation over time. It is considered a tangible asset with intrinsic value, but it also comes with risks such as market fluctuations and property management challenges.
Commodities
Commodities are raw materials or primary agricultural products that are traded on exchanges. Examples of commodities include gold, silver, oil, and agricultural products like wheat and corn. Investing in commodities can provide diversification benefits and a hedge against inflation, but prices can be volatile due to factors like supply and demand dynamics and geopolitical events.
Overall, each type of financial asset class offers a unique risk-return profile, and the key to successful investing is to create a well-balanced portfolio that aligns with your financial goals and risk tolerance. By diversifying across different asset classes, you can mitigate risk and maximize returns over the long term.
Investment Strategies for Financial Asset Classes
Investment strategies for financial asset classes play a crucial role in determining the success of an investment portfolio. It is essential to understand the different strategies available for each asset class in order to maximize returns and manage risks effectively.
Equities
- Buy and Hold Strategy: Investors purchase stocks with the intention of holding them for a long period of time, typically aiming to benefit from long-term capital appreciation.
- Value Investing: This strategy involves identifying undervalued stocks that have the potential to increase in value over time, based on fundamental analysis.
- Growth Investing: Investors focus on companies with strong growth prospects, even if they may be trading at a premium. The goal is to benefit from the stock price appreciation as the company grows.
Bonds
- Duration Matching: Investors match the duration of their bond investments with their investment time horizon to minimize interest rate risk.
- Income Investing: This strategy involves focusing on bonds that provide a regular income stream through interest payments, suitable for investors seeking stable cash flow.
- Laddering: Investors build a bond ladder by purchasing bonds with staggered maturities, allowing for regular reinvestment opportunities and reducing reinvestment risk.
Real Estate
- Rental Properties: Investors purchase properties to generate rental income, providing a steady cash flow stream over time.
- Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs): Investors can invest in REITs, which offer exposure to real estate markets without the need to directly own properties.
- Fix and Flip: This strategy involves purchasing properties, renovating them, and selling them for a profit in a short period of time.
Diversification Across Asset Classes
Diversification is a key strategy to reduce risk in an investment portfolio. By spreading investments across different asset classes, such as equities, bonds, and real estate, investors can minimize the impact of market volatility on their overall returns. It is important to maintain a balanced allocation based on investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon.
Influence of Economic Factors on Investment Decisions
Economic factors, such as interest rates, inflation, and geopolitical events, can significantly impact investment decisions across asset classes. For example, rising interest rates may negatively affect bond prices, while inflation can erode the purchasing power of equities. It is crucial for investors to stay informed about economic trends and adjust their investment strategies accordingly to navigate changing market conditions effectively.
Role of Financial Asset Classes in a Portfolio
When it comes to creating a well-diversified investment portfolio, the role of financial asset classes cannot be understated. Each asset class plays a unique part in helping investors achieve their financial goals and manage risk effectively.
Equities
Equities, or stocks, represent ownership in a company and offer the potential for high returns. Including equities in a portfolio can help investors benefit from capital appreciation and dividend income, but they also come with higher volatility compared to other asset classes.
Bonds
Bonds are debt securities issued by governments or corporations, providing a fixed income stream to investors. Including bonds in a portfolio can help reduce overall risk due to their relatively stable returns and inversely correlated movement to equities.
Real Estate
Real estate investments include properties such as residential, commercial, or industrial assets. Real estate can offer diversification benefits and a hedge against inflation, as well as the potential for rental income and capital appreciation.
Commodities
Commodities are physical assets like gold, oil, or agricultural products that can be traded in financial markets. Including commodities in a portfolio can provide a hedge against inflation, currency devaluation, or geopolitical risks, offering diversification benefits.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents include money market instruments or short-term securities with high liquidity and low risk. Holding cash in a portfolio provides stability and flexibility, allowing investors to take advantage of opportunities in the market or weather uncertain conditions.
Asset Allocation for Risk Management
Diversifying across different asset classes is essential for managing risk in a portfolio. By spreading investments across various asset classes with different risk-return profiles, investors can reduce the impact of market volatility and specific risks associated with a single asset class.
Impact of Market Conditions
Market conditions, such as economic indicators, interest rates, inflation, or geopolitical events, can significantly impact the performance of various asset classes. Understanding how different asset classes react to changing market conditions is crucial for making informed investment decisions and adjusting portfolio allocations accordingly.
